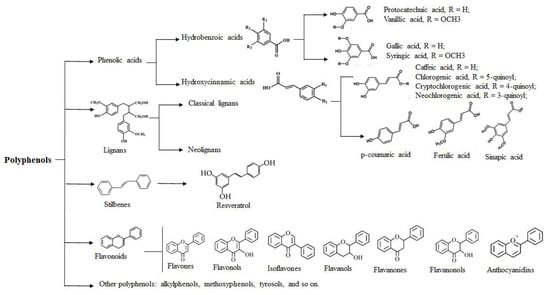
Effects of Natural Polyphenols on Skin and Hair Health: A Review
Source : https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/27/22/7832/htm
The skin is the largest organ of the body and plays multiple essential roles, ranging from regulating temperature, preventing infections, to ultimately affecting human health. A hair follicle is a...
Discussion: It is important to assess the effectiveness of polyphenolic compounds against skin and hair diseases applied systemically and/or topically. Despite the fact that polyphenols are multi-potent compounds that can be used in the treatment of a wide spectrum of diseases, including skin and hair diseases, some properties may limit their...
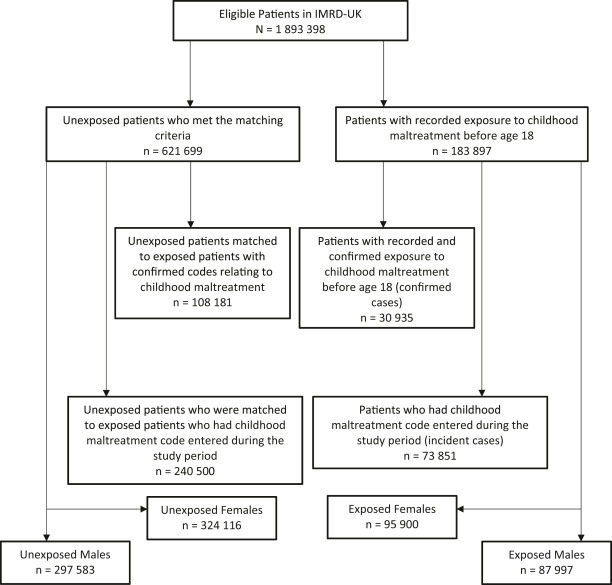
Association between childhood maltreatment and atopy in the UK: A population based retrospective cohort study
Source : https://www.thelancet.com/journals/eclinm/article/PIIS2589-5370(22)00460-6/fulltext
Considering the substantial health burden associated with childhood maltreatment, it is important to implement public health policies aimed at enhancing: 1) detection and primary prevention of childhood maltreatment, 2) secondary...
Discussion: Our study found that exposure to childhood maltreatment was associated with an increased risk of developing atopic disease. We also found a greater incidence rate of atopic disease in female patients exposed to childhood maltreatment in comparison to males.

Comparison of Pediatric Dermatology Conditions Across Telehealth and In-Person Visits During the COVID-19 Pandemic - PubMed
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36342725/
Understanding the utility of virtual visits in pediatric dermatology practice has become increasingly important in the telehealth era. We compared the conditions diagnosed in pediatric dermatology between traditional in-person visits...
Discussion: When given the option, pediatric dermatology patients and their families were more likely to choose telehealth visits for the diagnosis and/or management of acne, hemangiomas, and contact dermatitis; however, they were more likely to choose in-person visits for atopic dermatitis, viral warts, and alopecia areata. These differences...
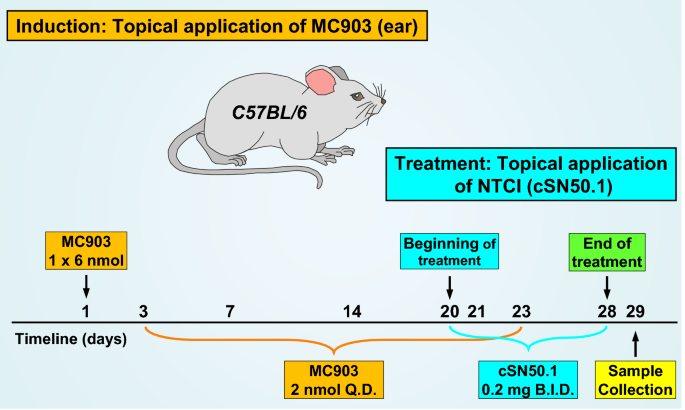
Genomic control of inflammation in experimental atopic dermatitis - Scientific Reports
Source : https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-23042-x
Atopic Dermatitis (AD) or eczema, a recurrent allergic inflammation of the skin, afflicts 10-20% of children and 5% adults of all racial and ethnic groups globally. We report a new...
Discussion: We show that NTCI effectively reduces the cardinal signs of AD in an experimental model. To our knowledge, this study is the first preclinical proof of concept for the genomic control of AD by NTCI at the nuclear transport level.
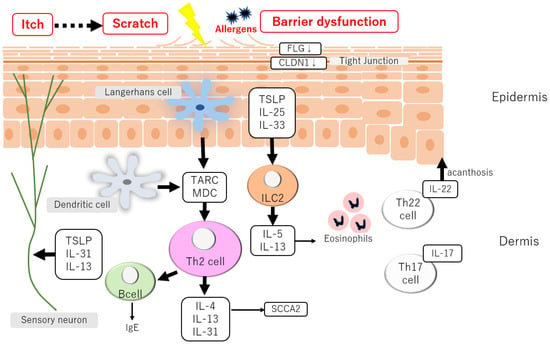
Involvement of Atopic Dermatitis in the Development of Systemic Inflammatory Diseases
Source : https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/23/21/13445/htm
The skin is recognized as a peripheral lymphoid organ that plays an essential defensive action against external environmental stimuli. However, continuous stimulation of these factors causes chronic inflammation at the...
Discussion: These findings suggest that atopic-mediated systemic organ inflammation negatively regulates the development of systemic inflammatory responses and organ dysfunction. Therefore, the key factors in the pathogenesis of AD and systemic inflammatory disorders highlight the importance of systemic treatment against atopic skin...

