Conclusion: People with AD have an increased risk of multiple autoimmune conditions, especially those with more severe AD.
Highlights:
• Tetrahydrocurcumin entrapped hybrid colloid as food additive was assembled and investigated.
• The oral administration of TCCHC can alleviate the symptoms of atopic dermatitis in NC/Nga animal model.
• TCCHC might be a promising new functional food additive for AD patients.

Novel Association of Lyme disease, Age, and Atopic Dermatitis
Source : https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.01.27.476641
Borrelia burgdorferi is a bacterial spirochete that can cause Lyme disease (LD) after infecting a susceptible host. Immune responses to the bacteria are highly variable and host specific. The murine...
Data from mice and humans reveal a novel relationship among LD, age, and atopic dermatitis. Through defined pathological scoring, we demonstrate that the onset of murine Lyme disease associated atopic dermatitis is exacerbated by increased host age at time of B. burgdorferi infection. In humans, a diagnosis of Lyme disease in FinnGen was...
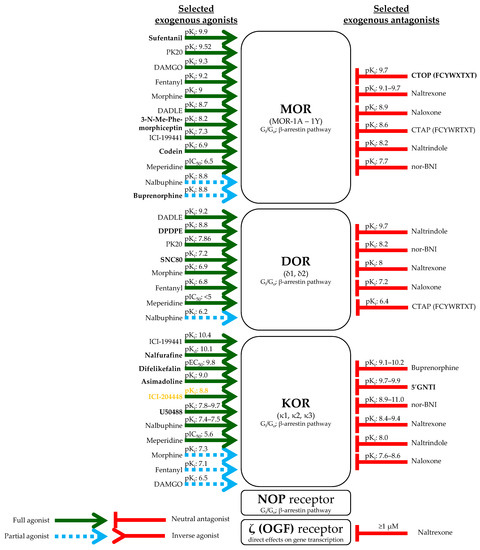
Opioidergic Signaling-A Neglected, Yet Potentially Important Player in Atopic Dermatitis
Source : https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23084140
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is one of the most common skin diseases, the prevalence of which is especially high among children. Although our understanding about its pathogenesis has substantially grown in...
It is commonly accepted that dysfunction of the complex cutaneous barrier plays a central role in the development of AD; therefore, the signaling pathways involved in the regulation of this quite complex process are likely to be involved in the pathogenesis of the disease and can provide novel, promising, yet unexplored therapeutic targets....

Comparing the psychometric properties of the EQ-5D-3L and EQ-5D-5L descriptive systems and utilities in atopic dermatitis - The European Journal of Health Economics
Source : https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10198-022-01460-y
Background Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a common chronic inflammatory skin disorder affecting up to 10% of adults. The EQ-5D is the most commonly used generic preference-accompanied measure to generate quality-adjusted...
Conclusion: Both instruments exhibited good psychometric properties in AD; however, the EQ-5D-5L was superior in terms of ceiling effects, informativity and convergent validity. We recommend the use of the EQ-5D-5L to measure health outcomes in clinical settings and for QALY calculations in AD.

